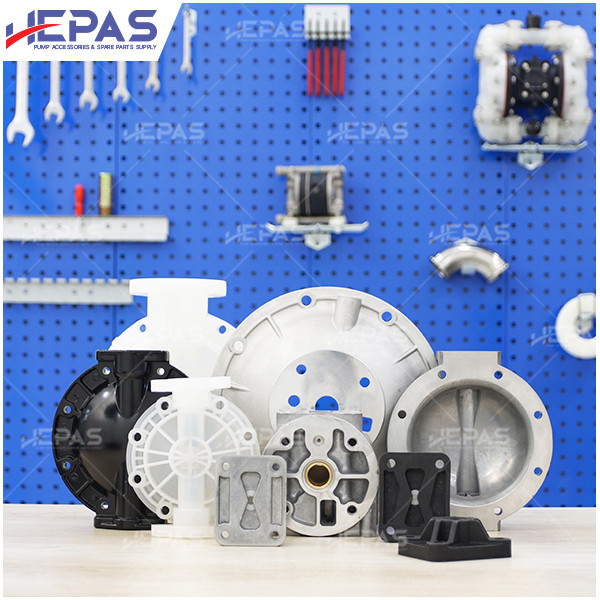
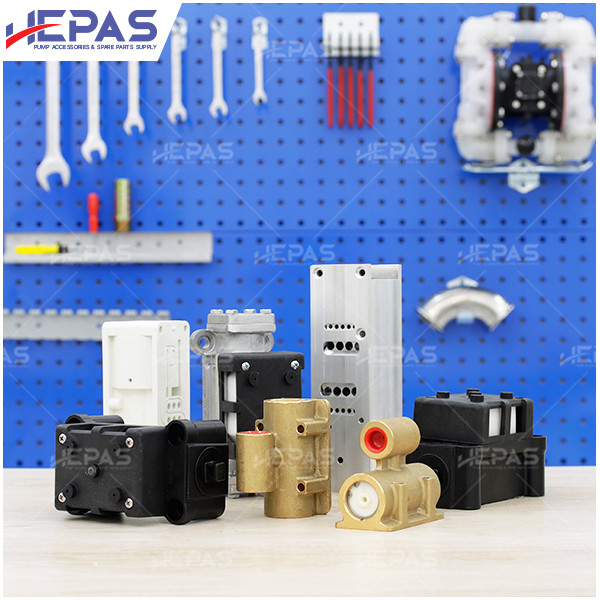
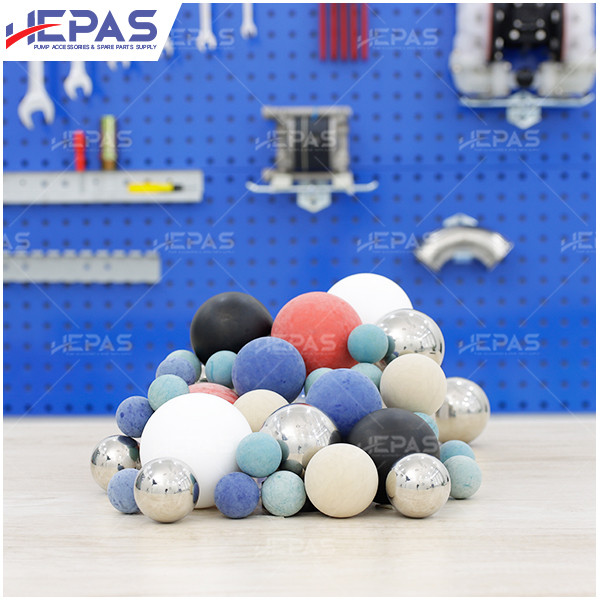
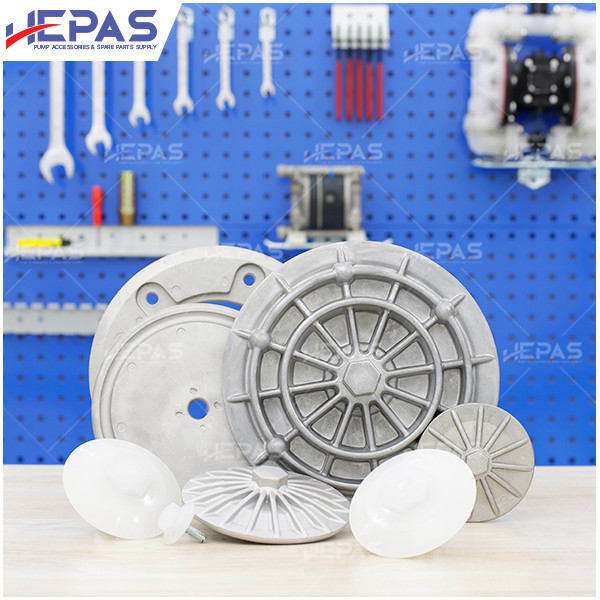
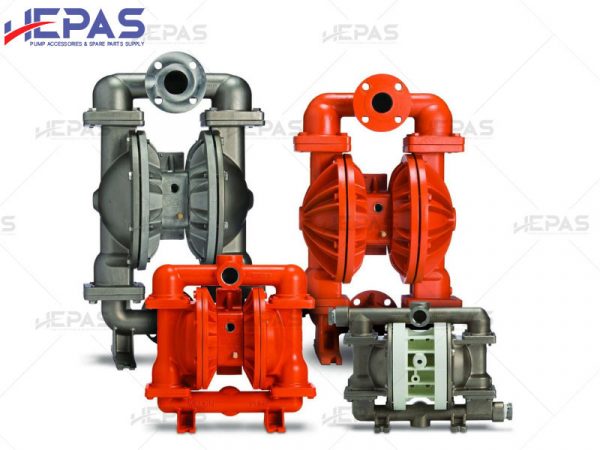
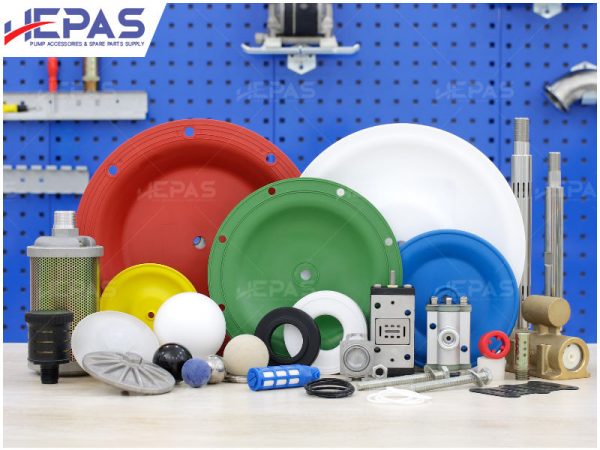
Replacement parts
Diaphragm pumps are essential devices used across various industries. Their simple yet effective operating principle makes them versatile for different applications. While diaphragm pumps generally have a longer lifespan than many other types of pumps, they can still be susceptible to damage when handling corrosive liquids. Regular inspection, maintenance, and replacement of spare parts are necessary to ensure optimal production efficiency.
A diaphragm pump is an industrial pump that operates using the back-and-forth movement of the pump diaphragms. There are two main types of diaphragm pumps: air-operated double diaphragm (AODD) pumps and electrically driven diaphragm pumps.
- AODD pumps utilize compressed air to exert pressure on the diaphragms, transferring the pressure to the fluid, and moving it through the pump.
- Electrically driven diaphragm pumps work by using an electric motor to create a continuous and alternating movement of the diaphragms.
These pumps are widely used in industrial applications because of their ability to self-prime, eliminating the need for manual priming like other conventional pumps. Additionally, air-operated double diaphragm pumps can run dry without generating heat, have affordable replacement parts, operate efficiently, and come in a variety of materials, making them suitable for a broad range of industrial applications.
Diaphragm pump is an industrial pump
(Source: Hepas)
How Diaphragm Pumps Work
Air-operated diaphragm pumps function based on the reciprocating motion of a piston. As the piston moves, it displaces the diaphragm, creating a suction and discharge pressure. Compressed air enters the air chambers, pushing the diaphragm outward, which allows the fluid to be sucked in and pushed out through the pump.
Components of a Diaphragm Pump
Diaphragm pumps are divided into two main sections:
- Fluid side: This is the part that comes into direct contact with the pumped liquid. It includes the manifold, diaphragm plates, pump ball, and ball seat.
- Airside: This section interacts with the compressed air and contains the air valve, air chambers, and other air-distributing parts.
More detailed components include:
- The pump body, which houses the liquid (also known as the liquid chamber)
- The diaphragm
- The pump ball and ball seat
- The air valve (or air distribution system)
- Mufflers to reduce noise
- Suction and discharge ports
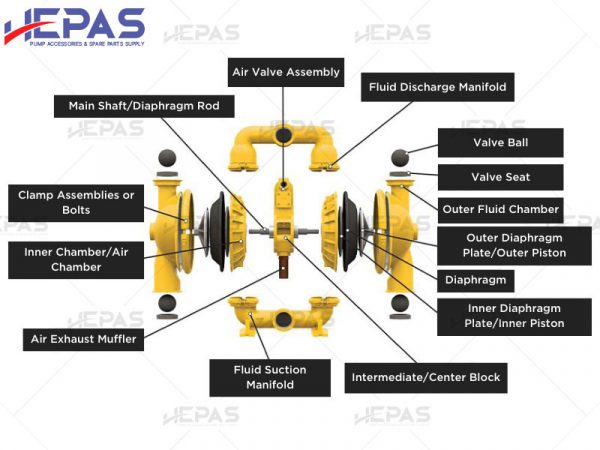
(Source: Hepas)
When to Replace Diaphragm Pump Parts
Diaphragms should be serviced every six months when handling highly corrosive liquids like acids and alkalis. In such environments, diaphragms are prone to tearing or puncturing over prolonged use.
For less aggressive applications like food processing or pumping slurry, the diaphragms can last up to a year before needing maintenance.
Other components such as the pump ball, ball cage, and air valve should also be checked every two years to ensure they are functioning properly, even if they do not directly contact the pumped liquid.
Additionally, it’s essential to monitor the pump’s operation. Check whether the fluid levels in the suction and discharge chambers meet the standards, and observe for any signs of abnormality in the pump’s performance.
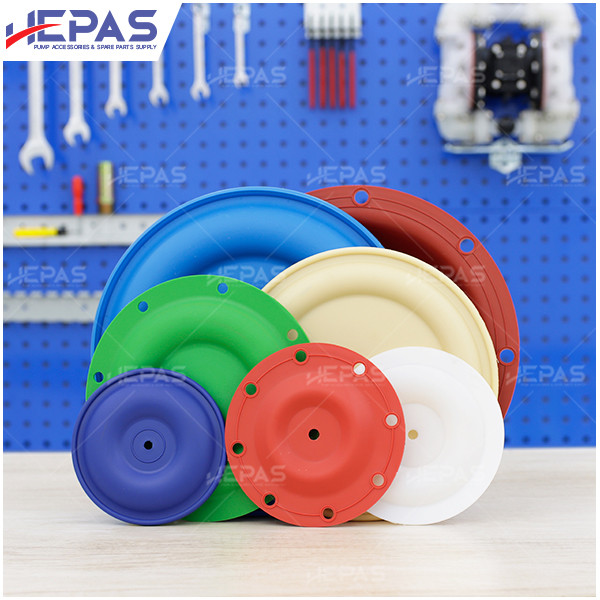
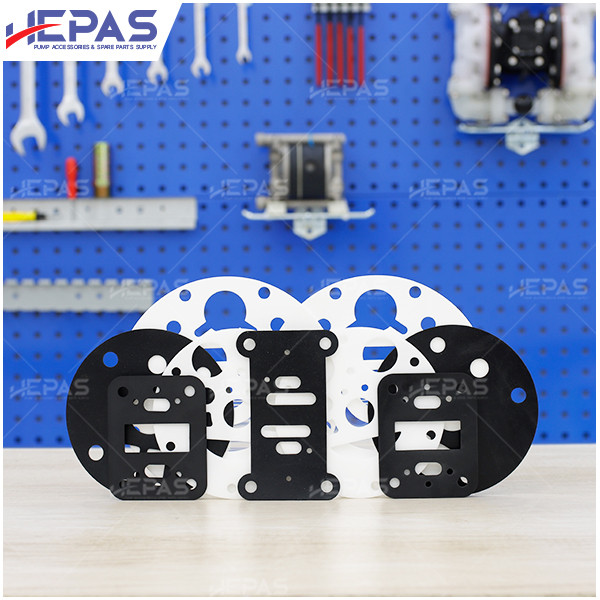
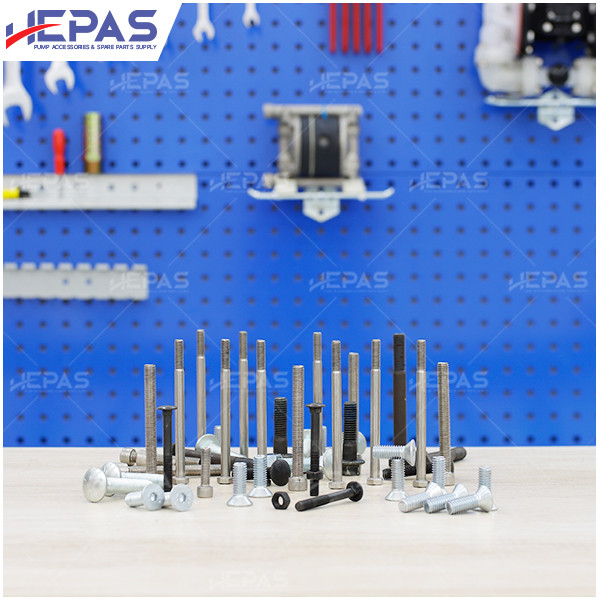
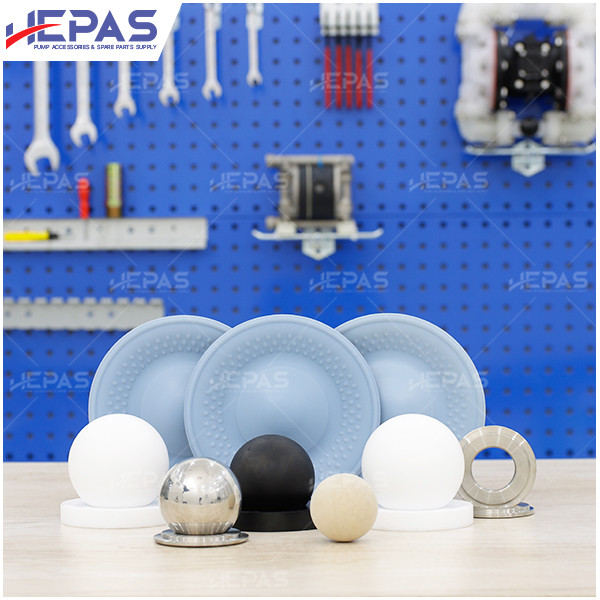
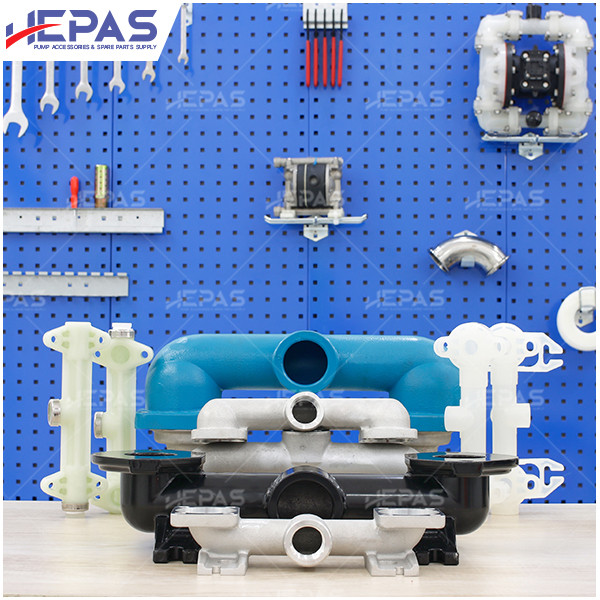
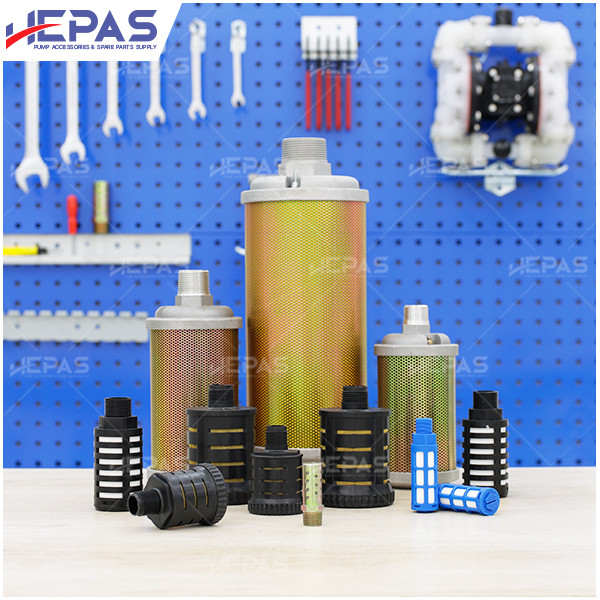
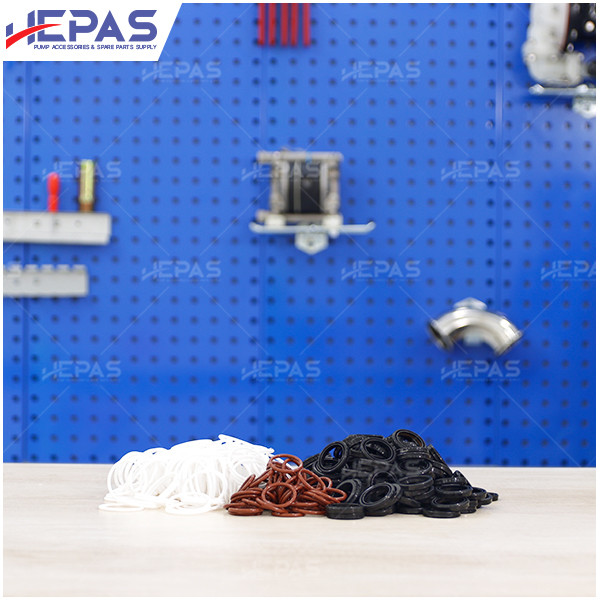
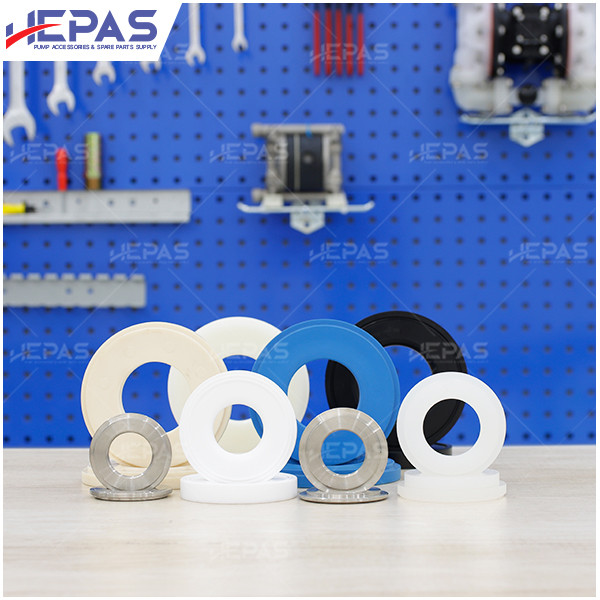
Replacement Parts for Diaphragm Pump
Several parts of the diaphragm pump may need frequent replacement due to their constant exposure to pumped liquids, leading to corrosion and damage:
- Pump body: While the pump body rarely fails, it must be selected based on the liquid being pumped. Materials like aluminum, stainless steel, and plastic are commonly used.
- Diaphragm: Diaphragms are more likely to wear out since they are in direct contact with the fluid. Common diaphragm materials include Santoprene, EPDM, Buna-N, Teflon, Viton, and Nitrile.
- Pump ball & ball seat: These components are in constant contact with the fluid and are prone to corrosion and damage. Thus, regular inspections and replacements are necessary.
- Air valve: The air valve, which distributes compressed air to both air chambers, plays a crucial role in pump operation and may need replacement when worn out.
- Other components such as pistons, gaskets, O-rings & U-cups, and mufflers should also be checked regularly to ensure smooth operation.
Parts That Fit Diaphragm Pumps
(Source: Hepas)
Conclusion
All machines, including diaphragm pumps, experience wear over time. Therefore, it is essential to regularly inspect and maintain the pump to address any issues and replace damaged parts such as diaphragms, pump balls, and air valves. If you need quality replacement parts for your diaphragm pump hardware, such as gaskets, pump sleeves, pump shafts, manifolds, or liquid chambers, feel free to contact us for assistance.


















